Zircon has the characteristics of low acidity, and high melting point, can be combined with all organic and inorganic sand binders, and can be used as a molding substrate for sand casting and investment casting. It is widely used in the fields of aerospace, military industry, nuclear reaction and atomic energy, and it is also an important mineral material in the advanced industry of national defense. With the rapid development of electronics, national defense technology, information industry and emerging materials industry, zirconium chemical products occupy an increasingly important position in high-tech fields at home and abroad, and the demand is growing rapidly.

Zircon, zircon sand, formerly known as zircon, hyacinth stone, transparent as a gemstone, also known as zircon gemstone. It is a mineral mainly composed of zirconium, silicon and oxygen crystallized from magma when igneous rocks are formed, and is also produced in dikes and metamorphic rocks. It is mostly symbiotic with ilmenite, rutile, monazite, xenotime, etc. in the coastal sand. Pure zircon sand is a colorless and transparent crystal, often dyed into yellow, orange, red, brown and other colors due to different origins and different types and quantities of impurities. Zircon sand has low thermal expansion, high thermal conductivity, and strong chemical stability.
Zircon Benficiation Process
Zircon beneficiation refers to the process of removing impurities in zircon ore and increasing the content of zircon. The following four beneficiation methods are often used: gravity separation, electrical separation, magnetic separation and flotation.
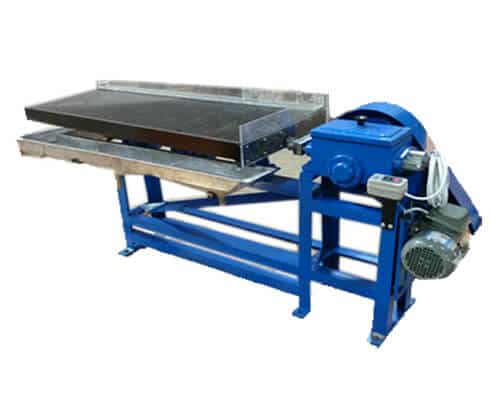
- Gravity separation
Zircon mostly occurs in ilmenite, and is often accompanied by heavy minerals such as hematite, chromite and garnet. Therefore, in the initial stage of enrichment of columbine, gravity separation is often used, such as using a shaking table to separate heavy minerals from gangue (quartz, feldspar, biotite), etc., and then use other beneficiation methods to separate them from other heavy minerals.
- Electric separation
Conductive minerals such as ilmenite, hematite, chromite, cassiterite, and rutile are separated from non-conductive minerals such as zircon, monazite, garnet, and apatite by utilizing the difference in mineral conductivity. Desliming, grading, drying and dosing should be done in advance before electrification.
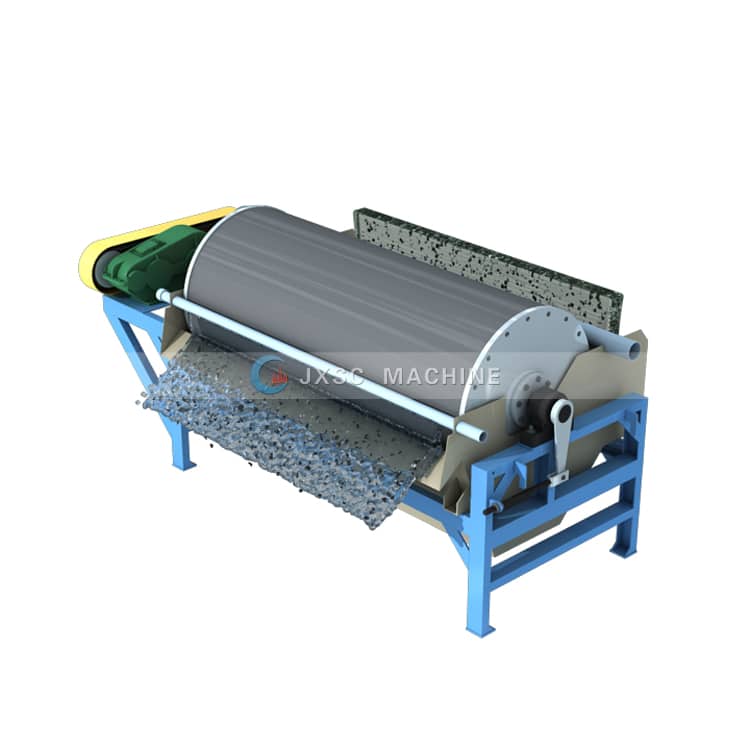
- Magnetic separation
Magnetic minerals in heavy minerals include ilmenite, hematite, chromite, garnet, biotite, monazite, etc. Zircon is a non-magnetic mineral or a weakly magnetic mineral (in some deposits, the iron in the zirconia is weakly magnetic). Magnetic separation is divided into two types: dry and wet. In dry magnetic separation, the selected materials need to be heated, dried, classified and other pre-treatment before sorting. The wet type strong magnetic field magnetic separator has a wide separation particle size, and the particle size lower limit can reach 20pm. Therefore, it is more appropriate to use a wet magnetic separator when the zircon particle size is fine.
- Flotation separation
Commonly used collectors are fatty acids (oleic acid, sodium oleate) and the like. The slurry modifier is sodium carbonate, the inhibitor is sodium silicate, and the activator is sodium sulfide and heavy metal salts (zirconium chloride, ferric chloride). Oxalic acid is also used to adjust the pulp to acidity, and amine collectors are used for flotation.
Zircon is mostly produced in coastal placer mines, and its associated minerals are mainly ilmenite, rutile, monazite, and sphene, and the gangue minerals are mainly quartz. Generally, when zircon is separated, these heavy minerals are also recovered as target minerals, which need to be combined with methods such as gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation, and electrical separation.

Zircon Beneficiation Process Flow Design
This is a 100 t/h beach sand processing plant, complete plant is configured with the below machines: feeder, vibrating screen, belt conveyor, slurry pump, magnetic separator, spiral chute, shaking table, dryer, electrostatic separator.
Raw ore information as below:
-Capacity 100tph
-Above 2mm impurities are removed
-Need separate rutile, monazite, zircon, ilmenite, magnetite from the beach sand
Flowchart explanation as below:
1. Excavator or Loader feed raw sand to raw ore bin, then through the electromagnetic vibrating feeder to feed vibrating screen.
2. Vibrating screen with one layer screen with 2mm mesh size, in order to remove above 2mm impurities.
3. Below 2mm go to magnetic separator by slurry pump for separating out magnetite
4. Output of magnetic separator is sent to spiral chute by a slurry pump. Through gravity separation method to remove light minerals.
5. Spiral chute gravity separation plant has two stages: the middling from the first stage spiral chute plant goes to the second stage spiral chute for reprocessing.
6. All concentrates from two stages spiral chute plants are sent to 1st double drum magnetic separator for separating out ilmenite.
7. Output of 1st double drum magnetic separator are sent to shaking table by slurry pump for removing light minerals by gravity principle.
8. Shaking table has two stages: the middling from the first stage shaking table is sent to the second stage shaking table for further processing by a slurry pump.
9. All concentrate from two stages shaking table plant is sent to the rotary dryer for drying material.
10. After drying, dry materials through hoist machine to 2nd double drum magnetic separator for separating out ilmenite.
11. Other minerals from 2nd double drum magnetic separator go to 1st electrostatic separator through hoist machine for separating out rutile, other minerals through hoist machine to 2nd electrostatic separator for separating out rutile, other minerals through hoist machine to 3rd electrostatic separator for separating out rutile.
12. Other minerals from the 3rd electrostatic separator go to the double roller strong magnetic separator via hoist machine for separating out zircon and monazite.
The zircon ore equipment, beneficiation method and technological process used in zircon beneficiation depend on factors such as deposit type, ore properties and mineral composition. Contact us for custom zircon mining process solutions.