Zircon Beach Sand Processing Plant
Posted on: Jul 5, 2019, · 3 min read.
What's zircon ore?
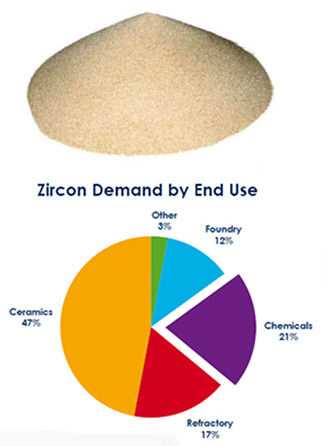 Zircon (also known as azorite) is zirconium orthosilicate, and its chemical formula is ZrSiO4, which is the most common type of zirconium-containing minerals. Most of the zircon deposits are seashore sand mines. Placer containing zircon, usually associate with magnetite, ilmenite, rutile, and monazite, etc. Generally, at the same time of selecting zircon, these placer minerals were also recovered as target minerals. Zircon applications Zircon is mainly used as a raw material for zirconate refractory bricks, and precision casting sand and ceramic tools. Zircon mineral is the most important mineral raw material for the extraction of zirconium and hafnium. It is also an important mineral material in the defense industry. The melting point of zircon is up to 3000 °C, which can be used as a material for spacecraft high temperature insulation tiles. Zircon is a gemstone with a refractive index second only to diamonds and a high dispersion value. The colorless and transparent zircon resembles a diamond and is a good substitute for diamonds. Resource and distribution The main producers of zircon in the world are South Africa, Australia, the United States, Indonesia and Brazil. China zircon is mainly produced in Guangdong, Hainan province.
Zircon (also known as azorite) is zirconium orthosilicate, and its chemical formula is ZrSiO4, which is the most common type of zirconium-containing minerals. Most of the zircon deposits are seashore sand mines. Placer containing zircon, usually associate with magnetite, ilmenite, rutile, and monazite, etc. Generally, at the same time of selecting zircon, these placer minerals were also recovered as target minerals. Zircon applications Zircon is mainly used as a raw material for zirconate refractory bricks, and precision casting sand and ceramic tools. Zircon mineral is the most important mineral raw material for the extraction of zirconium and hafnium. It is also an important mineral material in the defense industry. The melting point of zircon is up to 3000 °C, which can be used as a material for spacecraft high temperature insulation tiles. Zircon is a gemstone with a refractive index second only to diamonds and a high dispersion value. The colorless and transparent zircon resembles a diamond and is a good substitute for diamonds. Resource and distribution The main producers of zircon in the world are South Africa, Australia, the United States, Indonesia and Brazil. China zircon is mainly produced in Guangdong, Hainan province.
How to extract zircon from sand?
Zircon beneficiation is the process of removing impurities from zircon ore and increasing the zircon grade. Generally, zircon beneficiation methods includes gravity separation, magnetic separation, electrostatic selection and flotation.
Gravity separation Zircon is often found in ilmenite and is often associated with heavy minerals such as hematite, chromite and garnet. Therefore, the initial stage of extraction of zircon is often adopts gravity separation method, for example, the separation of heavy minerals from gangue (quartz, feldspar, biotite) by a shaker table. gravity separator for sale
Flotation The commonly used collectors for flotation are fatty acids (oleic acid, sodium oleate), etc.; the pulp regulator is sodium carbonate; the inhibitor is sodium silicate; the activator is sodium sulfide and heavy metal salts (zirconium chloride, ferric chloride) ). flotation separation price
Electric separation The conductive minerals such as ilmenite, hematite, chromite, cassiterite and rutile are separated from non-conductive minerals such as zircon, monazite, garnet and apatite by the difference in mineral conductivity. Prior to electric separation, desliming classification, drying and dosing should be carried out. What's electrostatic separator?
Magnetic separation The magnetic minerals are ilmenite, hematite, chromite, garnet, biotite, and monazite. Zircon is a non-magnetic mineral or a weakly magnetic mineral. Magnetic separation is divided into dry and wet type. For dry magnetic separation, the selected materials should be dried, classification by advance. Wet strong magnetic separator has a wide particle size and a lower particle size limit of 20um. Therefore, it is suitable to use a wet magnetic separator when the zircon grain size is fine. types of magnetic separator Because there are many associated minerals in zircon ore, it needs to be combined by gravity separation, magnetic separation, flotation, and electric selection. Zircon's beneficiation process is closely related to the associated beneficial mineral types.
| Associate minerals | Processing flow |
| Rutile, zircon | Electrostatic - magnetic - flotation separation |
| Monazite, zircon | Magnetic - shaker table - magnetic separation |
| Cassiterite, monazite, rutile, zircon | Magnetic - shaker table - magnetic - shaker table - electrostatic - magnetic separation |
Zircon beneficiation processing methods are often divided into wet and dry type processes. The raw ore is first treated with wet type processing, and the gangue minerals such as quartz, feldspar and mica are removed by gravity separation equipment such as cone concentrator, spiral concentrator, shaker table or mineral jig. The obtained heavy minerals (coarse concentrate) are further separated from the remaining light minerals after 2 to 4 stages, and then concentrated, dehydrated, dried, cooled and sent to the dry processing section for further sorting.
The dry processing section generally consists of weak magnetic separation, strong magnetic separation and electrostatic selection. Its purpose is to comprehensively recover minerals such as magnetite, ilmenite, rutile and monazite that are associated with zircon. According to the difference of mineral magnetism and conductivity, magnetite can be recovered by weak magnetic separation; ilmenite and garnet can be recovered by strong magnetic separation; finally, monazite, rutile and zircon are separated by high-voltage electrostatic concentrator.
Cases
Take our Australia customer zircon processing plant as the example. Location: Western Australia Type: beach sand Heavy mineral content: 12% ~ 15%, ilmenite accounted for 75%, white titanium stone and zircon accounted for 10%, rutile accounted for 1%, monazite accounted for 0.5%. The wet processing sector is located on the floating vessel. The raw ore is first sieved to remove the useless rock, and then dehydrated, de-sludged by a hydrocyclone, and fed into a conical concentrator for rough selection.
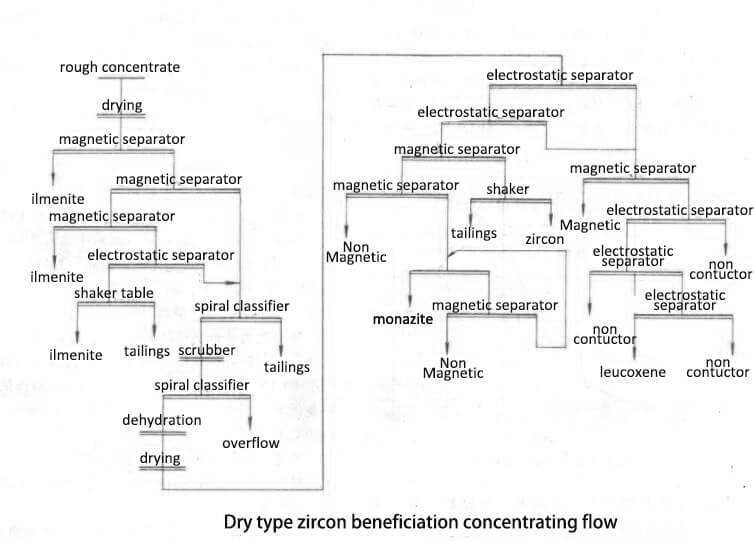
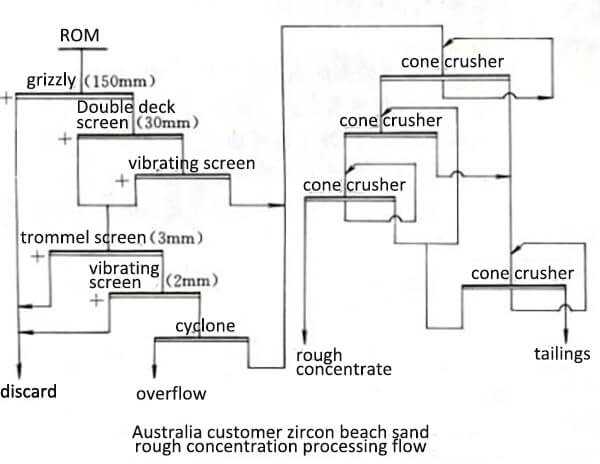 The useful minerals in the rough concentrate are mainly ilmenite. In the selection stage, the ilmenite is first selected by a dry magnetic separator. After the titanium is selected, the material is sorted by a spiral concentrator to further discharge the light minerals. After drying, electro-selection, magnetic separation and re-election are carried out to select monazite, zircon, ilmenite and other products. Tailings management, slurry pump for sale - Walker pump
The useful minerals in the rough concentrate are mainly ilmenite. In the selection stage, the ilmenite is first selected by a dry magnetic separator. After the titanium is selected, the material is sorted by a spiral concentrator to further discharge the light minerals. After drying, electro-selection, magnetic separation and re-election are carried out to select monazite, zircon, ilmenite and other products. Tailings management, slurry pump for sale - Walker pump
JXSC supply complete equipment for various mineral sands mining application, mineral ore processing plant. Are you facing machine configuration and layout design series zircon sand mining problems? We are here to help!
Read More Blogs